mirror of
https://github.com/RetroDECK/Duckstation.git
synced 2024-12-12 15:35:38 +00:00
206 lines
9.6 KiB
Markdown
206 lines
9.6 KiB
Markdown
|
|
xxHash - Extremely fast hash algorithm
|
||
|
|
======================================
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
<!-- TODO: Update. -->
|
||
|
|
xxHash is an Extremely fast Hash algorithm, running at RAM speed limits.
|
||
|
|
It successfully completes the [SMHasher](https://code.google.com/p/smhasher/wiki/SMHasher) test suite
|
||
|
|
which evaluates collision, dispersion and randomness qualities of hash functions.
|
||
|
|
Code is highly portable, and hashes are identical on all platforms (little / big endian).
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|Branch |Status |
|
||
|
|
|------------|---------|
|
||
|
|
|master | [](https://travis-ci.org/Cyan4973/xxHash?branch=master) |
|
||
|
|
|dev | [](https://travis-ci.org/Cyan4973/xxHash?branch=dev) |
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Benchmarks
|
||
|
|
-------------------------
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
The benchmark uses SMHasher speed test, compiled with Visual 2010 on a Windows Seven 32-bit box.
|
||
|
|
The reference system uses a Core 2 Duo @3GHz
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
| Name | Speed | Quality | Author |
|
||
|
|
|---------------|--------------------|:-------:|-------------------|
|
||
|
|
| [xxHash] | 5.4 GB/s | 10 | Y.C. |
|
||
|
|
| MurmurHash 3a | 2.7 GB/s | 10 | Austin Appleby |
|
||
|
|
| SBox | 1.4 GB/s | 9 | Bret Mulvey |
|
||
|
|
| Lookup3 | 1.2 GB/s | 9 | Bob Jenkins |
|
||
|
|
| CityHash64 | 1.05 GB/s | 10 | Pike & Alakuijala |
|
||
|
|
| FNV | 0.55 GB/s | 5 | Fowler, Noll, Vo |
|
||
|
|
| CRC32 | 0.43 GB/s † | 9 | |
|
||
|
|
| MD5-32 | 0.33 GB/s | 10 | Ronald L.Rivest |
|
||
|
|
| SHA1-32 | 0.28 GB/s | 10 | |
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
[xxHash]: https://www.xxhash.com
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Note †: SMHasher's CRC32 implementation is known to be slow. Faster implementations exist.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Q.Score is a measure of quality of the hash function.
|
||
|
|
It depends on successfully passing SMHasher test set.
|
||
|
|
10 is a perfect score.
|
||
|
|
Algorithms with a score < 5 are not listed on this table.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
A more recent version, XXH64, has been created thanks to [Mathias Westerdahl](https://github.com/JCash),
|
||
|
|
which offers superior speed and dispersion for 64-bit systems.
|
||
|
|
Note however that 32-bit applications will still run faster using the 32-bit version.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
SMHasher speed test, compiled using GCC 4.8.2, on Linux Mint 64-bit.
|
||
|
|
The reference system uses a Core i5-3340M @2.7GHz
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
| Version | Speed on 64-bit | Speed on 32-bit |
|
||
|
|
|------------|------------------|------------------|
|
||
|
|
| XXH64 | 13.8 GB/s | 1.9 GB/s |
|
||
|
|
| XXH32 | 6.8 GB/s | 6.0 GB/s |
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
This project also includes a command line utility, named `xxhsum`, offering similar features to `md5sum`,
|
||
|
|
thanks to [Takayuki Matsuoka](https://github.com/t-mat)'s contributions.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### License
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
The library files `xxhash.c` and `xxhash.h` are BSD licensed.
|
||
|
|
The utility `xxhsum` is GPL licensed.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### New hash algorithms
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Starting with `v0.7.0`, the library includes a new algorithm named `XXH3`,
|
||
|
|
which is able to generate 64 and 128-bit hashes.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
The new algorithm is much faster than its predecessors for both long and small inputs,
|
||
|
|
which can be observed in the following graphs:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
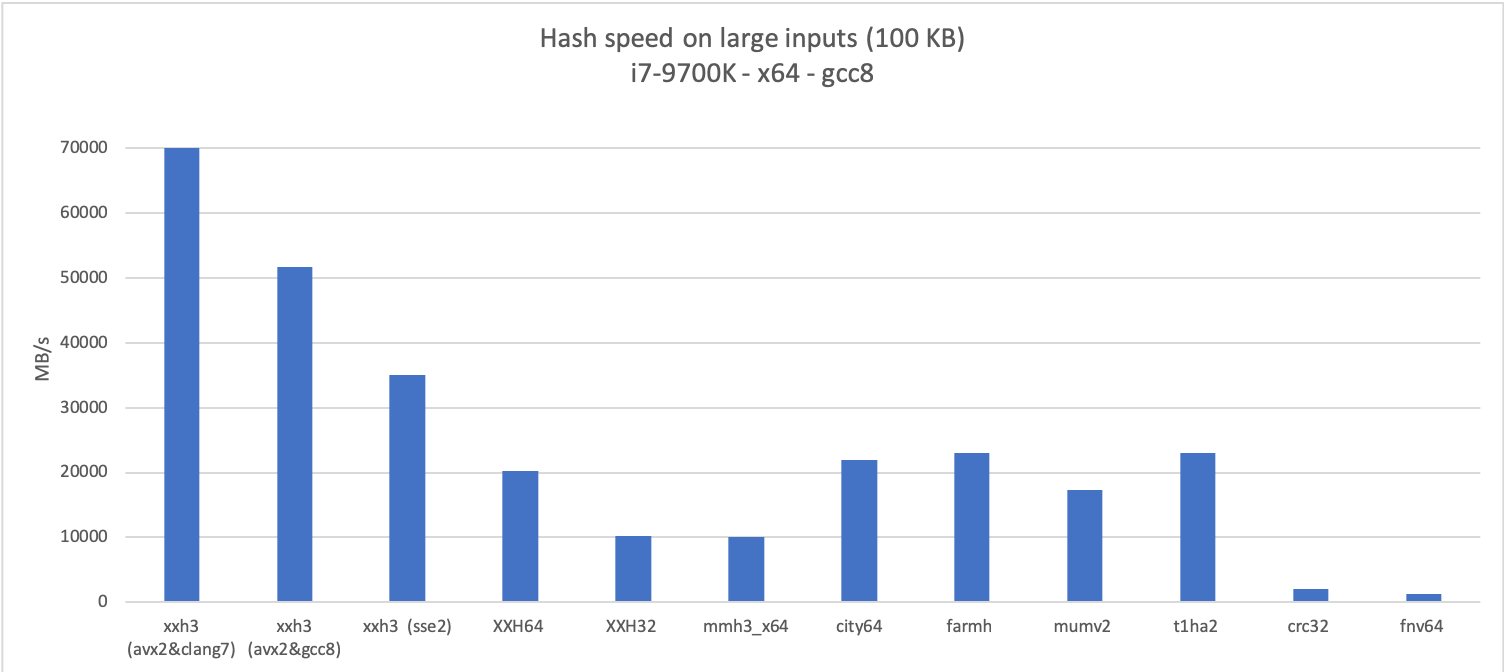
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
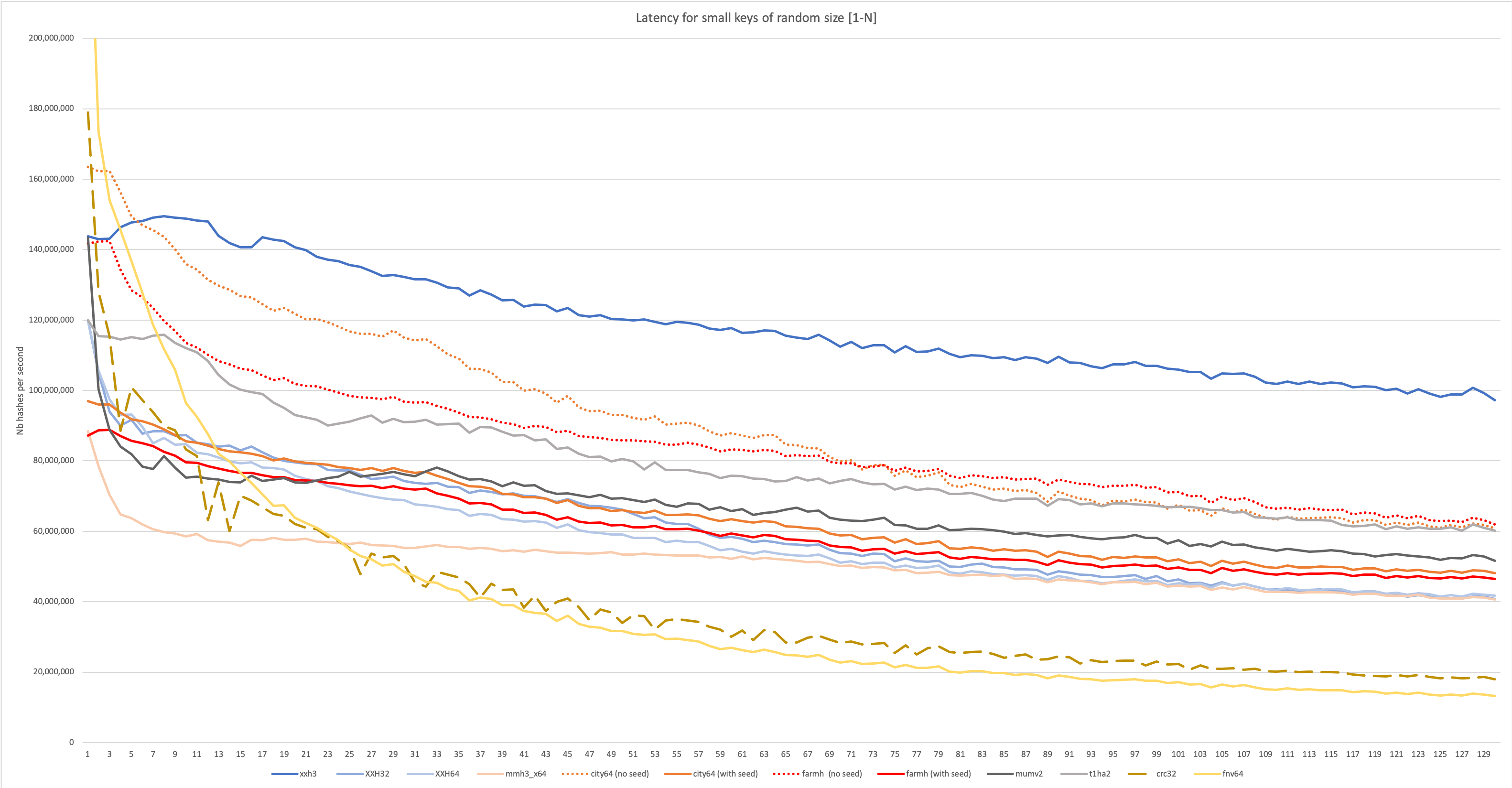
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
To access these new prototypes, one needs to unlock their declaration, using the build macro `XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY`.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
The algorithm is currently in development, meaning its return values might still change in future versions.
|
||
|
|
However, the API is stable, and can be used in production, typically for ephemeral
|
||
|
|
data (produced and consumed in same session).
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
`XXH3`'s return values will be finalized upon reaching `v0.8.0`.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Build modifiers
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
The following macros can be set at compilation time to modify libxxhash's behavior. They are all disabled by default.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
- `XXH_INLINE_ALL`: Make all functions `inline`, with implementations being directly included within `xxhash.h`.
|
||
|
|
Inlining functions is beneficial for speed on small keys.
|
||
|
|
It's _extremely effective_ when key length is expressed as _a compile time constant_,
|
||
|
|
with performance improvements being observed in the +200% range .
|
||
|
|
See [this article](https://fastcompression.blogspot.com/2018/03/xxhash-for-small-keys-impressive-power.html) for details.
|
||
|
|
Note: there is no need to compile an `xxhash.o` object file in this case.
|
||
|
|
- `XXH_NO_INLINE_HINTS`: By default, xxHash uses tricks like `__attribute__((always_inline))` and `__forceinline` to try and improve performance at the cost of code size. Defining this to 1 will mark all internal functions as `static`, allowing the compiler to decide whether to inline a function or not. This is very useful when optimizing for the smallest binary size, and it is automatically defined when compiling with `-O0`, `-Os`, `-Oz`, or `-fno-inline` on GCC and Clang. This may also increase performance depending on the compiler and the architecture.
|
||
|
|
- `XXH_REROLL`: Reduces the size of the generated code by not unrolling some loops. Impact on performance may vary, depending on the platform and the algorithm.
|
||
|
|
- `XXH_ACCEPT_NULL_INPUT_POINTER`: if set to `1`, when input is a `NULL` pointer,
|
||
|
|
xxHash'd result is the same as a zero-length input
|
||
|
|
(instead of a dereference segfault).
|
||
|
|
Adds one branch at the beginning of the hash.
|
||
|
|
- `XXH_FORCE_MEMORY_ACCESS`: The default method `0` uses a portable `memcpy()` notation.
|
||
|
|
Method `1` uses a gcc-specific `packed` attribute, which can provide better performance for some targets.
|
||
|
|
Method `2` forces unaligned reads, which is not standards compliant, but might sometimes be the only way to extract better read performance.
|
||
|
|
Method `3` uses a byteshift operation, which is best for old compilers which don't inline `memcpy()` or big-endian systems without a byteswap instruction
|
||
|
|
- `XXH_CPU_LITTLE_ENDIAN`: By default, endianess is determined at compile time.
|
||
|
|
It's possible to skip auto-detection and force format to little-endian, by setting this macro to 1.
|
||
|
|
Setting it to 0 forces big-endian.
|
||
|
|
- `XXH_PRIVATE_API`: same impact as `XXH_INLINE_ALL`.
|
||
|
|
Name underlines that XXH_* symbols will not be exported.
|
||
|
|
- `XXH_NAMESPACE`: Prefixes all symbols with the value of `XXH_NAMESPACE`.
|
||
|
|
Useful to evade symbol naming collisions,
|
||
|
|
in case of multiple inclusions of xxHash's source code.
|
||
|
|
Client applications can still use the regular function name,
|
||
|
|
as symbols are automatically translated through `xxhash.h`.
|
||
|
|
- `XXH_STATIC_LINKING_ONLY`: gives access to the state declaration for static allocation.
|
||
|
|
Incompatible with dynamic linking, due to risks of ABI changes.
|
||
|
|
- `XXH_NO_LONG_LONG`: removes support for XXH3 and XXH64 for targets without 64-bit support.
|
||
|
|
- `XXH_IMPORT`: MSVC specific: should only be defined for dynamic linking, as it prevents linkage errors.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Building xxHash - Using vcpkg
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
You can download and install xxHash using the [vcpkg](https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg) dependency manager:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
git clone https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg.git
|
||
|
|
cd vcpkg
|
||
|
|
./bootstrap-vcpkg.sh
|
||
|
|
./vcpkg integrate install
|
||
|
|
./vcpkg install xxhash
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
The xxHash port in vcpkg is kept up to date by Microsoft team members and community contributors. If the version is out of date, please [create an issue or pull request](https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg) on the vcpkg repository.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Example
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Calling xxhash 64-bit variant from a C program:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```C
|
||
|
|
#include "xxhash.h"
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
(...)
|
||
|
|
XXH64_hash_t hash = XXH64(buffer, size, seed);
|
||
|
|
}
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Using streaming variant is more involved, but makes it possible to provide data incrementally:
|
||
|
|
```C
|
||
|
|
#include "stdlib.h" /* abort() */
|
||
|
|
#include "xxhash.h"
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
XXH64_hash_t calcul_hash_streaming(FileHandler fh)
|
||
|
|
{
|
||
|
|
/* create a hash state */
|
||
|
|
XXH64_state_t* const state = XXH64_createState();
|
||
|
|
if (state==NULL) abort();
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
size_t const bufferSize = SOME_SIZE;
|
||
|
|
void* const buffer = malloc(bufferSize);
|
||
|
|
if (buffer==NULL) abort();
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
/* Initialize state with selected seed */
|
||
|
|
XXH64_hash_t const seed = 0; /* or any other value */
|
||
|
|
if (XXH64_reset(state, seed) == XXH_ERROR) abort();
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
/* Feed the state with input data, any size, any number of times */
|
||
|
|
(...)
|
||
|
|
while ( /* any condition */ ) {
|
||
|
|
size_t const length = get_more_data(buffer, bufferSize, fh);
|
||
|
|
if (XXH64_update(state, buffer, length) == XXH_ERROR) abort();
|
||
|
|
(...)
|
||
|
|
}
|
||
|
|
(...)
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
/* Get the hash */
|
||
|
|
XXH64_hash_t const hash = XXH64_digest(state);
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
/* State can be re-used; in this example, it is simply freed */
|
||
|
|
free(buffer);
|
||
|
|
XXH64_freeState(state);
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
return hash;
|
||
|
|
}
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Other programming languages
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Aside from the C reference version,
|
||
|
|
xxHash is also available in many different programming languages,
|
||
|
|
thanks to many great contributors.
|
||
|
|
They are [listed here](https://www.xxhash.com/#other-languages).
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Branch Policy
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
> - The "master" branch is considered stable, at all times.
|
||
|
|
> - The "dev" branch is the one where all contributions must be merged
|
||
|
|
before being promoted to master.
|
||
|
|
> + If you plan to propose a patch, please commit into the "dev" branch,
|
||
|
|
or its own feature branch.
|
||
|
|
Direct commit to "master" are not permitted.
|